Page 169 - Vitamin D and Cancer
P. 169
156 E. Gocek and G.P. Studzinski
leukemia cell differentiation were very comprehensively developed by Koeffler and
his various collaborators [148–151]. Their impressive achievements are described
in the preceding chapter in this volume. Accordingly, what follows in the remainder
of this section is an outline of the signaling mechanisms of AML cells that have
occupied the attention of the corresponding author’s laboratory.
In these studies, the laboratory has focused on HL60 cells, a widely available
cell line derived from a patient with promyeloblastic leukemia, with the objective
of achieving with the currently available tools as clear a picture as possible of the
signaling of monocytic differentiation. In this model, outlined in Figs. 7.3 and 7.4,
a plausible sequence of events is presented, but it is likely that other pathways are
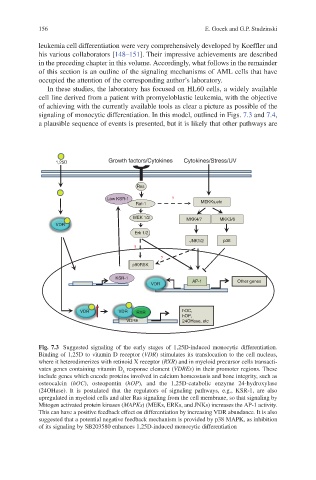
1,25D Growth factors/Cytokines Cytokines/Stress/UV
Ras
Low KSR-1 ?
Raf-1 MEKKs,etc
MEK 1/2 MKK4/7 MKK3/6
VDR
Erk 1/2
JNK1/2 p38
?
?
p90RSK
KSR-1 AP-1 Other genes
VDR
VDR VDR RXR hOC,
hOP,
VDRE 24OHase, etc
Fig. 7.3 Suggested signaling of the early stages of 1,25D-induced monocytic differentiation.
Binding of 1,25D to vitamin D receptor (VDR) stimulates its translocation to the cell nucleus,
where it heterodimerizes with retinoid X receptor (RXR) and in myeloid precursor cells transacti-
vates genes containing vitamin D response element (VDREs) in their promoter regions. These
3
include genes which encode proteins involved in calcium homeostasis and bone integrity, such as
osteocalcin (hOC), osteopontin (hOP), and the 1,25D-catabolic enzyme 24-hydroxylase
(24OHase). It is postulated that the regulators of signaling pathways, e.g., KSR-1, are also
upregulated in myeloid cells and alter Ras signaling from the cell membrane, so that signaling by
Mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) (MEKs, ERKs, and JNKs) increases the AP-1 activity.
This can have a positive feedback effect on differentiation by increasing VDR abundance. It is also
suggested that a potential negative feedback mechanism is provided by p38 MAPK, as inhibition
of its signaling by SB203580 enhances 1,25D-induced monocytic differentiation