Page 210 - Vitamin D and Cancer
P. 210
9 Molecular Biology of Vitamin D Metabolism and Skin Cancer 197
Non-genomic
PKA pathway
Secondary
1,25(OH) 2 D 3 PI3K pathway
messengers Raf-MEK-MAPK-ERK cascade
PKC pathway
VDR mem or
MARRS
protein Genomic
VDR
RXR Cross-talk
1,25(OH) 2 D 3 1,25(OH) 2 D 3
p
Nucleus
HDAC
complex CBP/300 NCoA62-SKIP
Methylation NCoR SMRT SRC
NCoA62-SKIP
VDR VDIR X VDR DRIPs RNA
RXR RXR
1,25(OH) 2 D 3 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 TFIIB Pol II
Plasma
membrane 5’ p nVDRE VDRE p 3’
Gene repression Gene expression
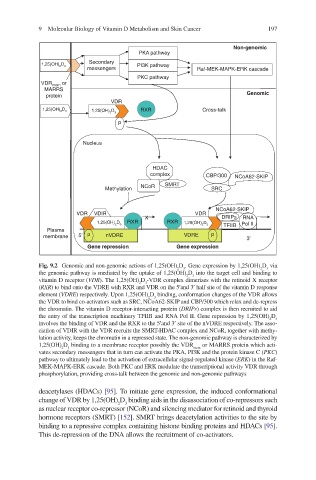
Fig. 9.2 Genomic and non-genomic actions of 1,25(OH) D . Gene expression by 1,25(OH) D via
3
2
2
3
the genomic pathway is mediated by the uptake of 1,25(OH) D into the target cell and binding to
3
2
vitamin D receptor (VDR). The 1,25(OH) D -VDR complex dimerizes with the retinoid X receptor
3
2
(RXR) to bind onto the VDRE with RXR and VDR on the 5¢and 3¢ half site of the vitamin D response
element (VDRE) respectively. Upon 1,25(OH) D binding, conformation changes of the VDR allows
2
3
the VDR to bind co-activators such as SRC, NCoA62-SKIP and CBP/300 which relax and de-repress
the chromatin. The vitamin D receptor-interacting protein (DRIPs) complex is then recruited to aid
the entry of the transcription machinery TFIIB and RNA Pol II. Gene repression by 1,25(OH) D
2
3
involves the binding of VDR and the RXR to the 5¢and 3¢ site of the nVDRE respectively. The asso-
ciation of VDIR with the VDR recruits the SMRT-HDAC complex and NCoR, together with methy-
lation activity, keeps the chromatin in a repressed state. The non-genomic pathway is characterized by
1,25(OH) D binding to a membrane receptor possibly the VDR mem or MARRS protein which acti-
3
2
vates secondary messengers that in turn can activate the PKA, PI3K and the protein kinase C (PKC)
pathway to ultimately lead to the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in the Raf-
MEK-MAPK-ERK cascade. Both PKC and ERK modulate the transcriptional activity VDR through
phosphorylation, providing cross-talk between the genomic and non-genomic pathways
deacetylases (HDACs) [95]. To initiate gene expression, the induced conformational
change of VDR by 1,25(OH) D binding aids in the disassociation of co-repressors such
2
3
as nuclear receptor co-repressor (NCoR) and silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid
hormone receptors (SMRT) [152]. SMRT brings deacetylation activities to the site by
binding to a repressive complex containing histone binding proteins and HDACs [95].
This de-repression of the DNA allows the recruitment of co-activators.