Page 25 - Vitamin D and Cancer
P. 25
12 H.S. Cross
Enhanced synthesis and accumulation of 1,25-(OH) D in the colon mucosa would
2 3
be responsible for up-regulation of transcriptional activity of CYP24A1 [34] and
also for autocrine/paracrine inhibition of tumor cell growth. We suggest that this
enhanced expression of CYP27B1 could be due, at least in part, to epigenetic regu-
lation, i.e., demethylation, while raised CYP24A1 expression probably results from
the normal regulatory loop following accumulation of 1,25-(OH) D in colonic
2 3
mucosa. However, in highly malignant tumors, an efficient antimitogenic effect by
1,25-(OH) D is unlikely, because expression of the catabolic vitamin D hydroxy-
2 3
lase by far exceeds that of CYP27B1. Our hypothesis, therefore, is that during
cancer progression CYP27B1 would be inactivated by epigenetic mechanisms,
whereas that of CYP24A1 would be activated. To test this, we studied expression
of vitamin D hydroxylases in 105 colon tumor patients entering a Viennese hospital
for tumor resection. Uncoupling of CYP24A1 expression from regulation by
colonic 1,25-(OH) D would lead to vitamin D hydroxylase expression in opposite
2 3
directions during progression to a highly malignant state. This is actually the case:
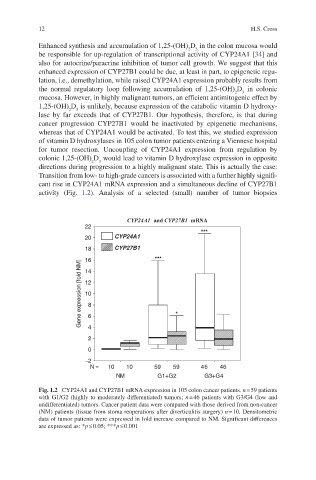
Transition from low- to high-grade cancers is associated with a further highly signifi-
cant rise in CYP24A1 mRNA expression and a simultaneous decline of CYP27B1
activity (Fig. 1.2). Analysis of a selected (small) number of tumor biopsies
CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 mRNA
22
***
20 CYP24A1
18 CYP27B1
NM] 16 ***
14
[fold 12
Gene expression 10 8 6 *
2 4
0
–2
N = 10 10 59 59 4 6 46
NM G1+G2 G3+G4
Fig. 1.2 CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 mRNA expression in 105 colon cancer patients. n = 59 patients
with G1/G2 (highly to moderately differentiated) tumors; n = 46 patients with G3/G4 (low and
undifferentiated) tumors. Cancer patient data were compared with those derived from non-cancer
(NM) patients (tissue from stoma reoperations after diverticulitis surgery) n = 10. Densitometric
data of tumor patients were expressed in fold increase compared to NM. Significant differences
are expressed as: *p £ 0.05; ***p £ 0.001