Page 241 - Vitamin D and Cancer
P. 241
228 C.M. Barnett and T.M. Beer
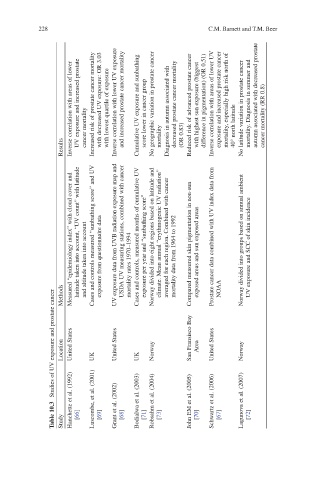
Inverse correlation with areas of lower UV exposure and increased prostate Increased risk of prostate cancer mortality with decreased UV exposure: OR 3.03 with lowest quartile of exposure Inverse correlation with lower UV exposure and increased prostate cancer mortality Cumulative UV exposure and sunbathing score lower
Results cancer mortality mortality (OR 0.83)
Measured “epidemiology index” with cloud cover and
and altitude taken into account latitude taken into account, “UV count” with latitude Cases and controls measured “sunbathing score” and UV exposure from questionnaire data UV exposure data from UVB radiation exposure map and USDA UV measuring stations, combined with cancer mortality rates 1970–1994 Cases and controls
Methods
Studies of UV exposure and prostate cancer Location United States UK United States UK Norway San Fransisco Bay Area United States Norway
Table 10.3 Study Hanchette et al. (1992) [66] Luscombe, et al. (2001) [69] Grant et al. (2002) [68] Bodialwa et al. (2003) [71] Robsahm et al. (2004) [73] John EM et al. (2005) [70] Schwartz et al. (2006) [67] Lagunova et al. (2007) [72]